Lineage tracing for general data warehouse transformations
- 2 minsReference: paper
Lineage tracing is the problem of tracing warehouse data items to the original source items from which they were derived. Lineage tracing has several applications, such as authorization management and in-depth data mining. In this work, authors define the lineage tracing problem in the presence of general data warehouse transformations and present a tracing algorithm applicable to single transformations, linear sequences of transformations, and arbitrary acyclic transformation graphs.
Transformation
Let a data set be a set of data items – tuples, values, or complex objects. A transformation is any procedure that takes data sets as input and produces data sets as output. For any input data set I, we say that the application of T to I resulting in an output set O, T(I)=O, is an instance of T.
Given transformations T1 and T2, their composition T=T1T2 first applies T1 to I to obtain I’, and then applies T2 to I’ to obtain O. T1 and T2 are *component transformations. A composition that is not defined as a composition of other transformations is atomic.
Data lineage
A data item o in the output set may have been derived from a small subset of the input data items. The actual set I* of input data items that contributed to o’s derivation is the lineage of o, denoted with I* = T*(o, I). The lineage of a set of output data items is the union of the lineage of each item in the set.
Transformation properties
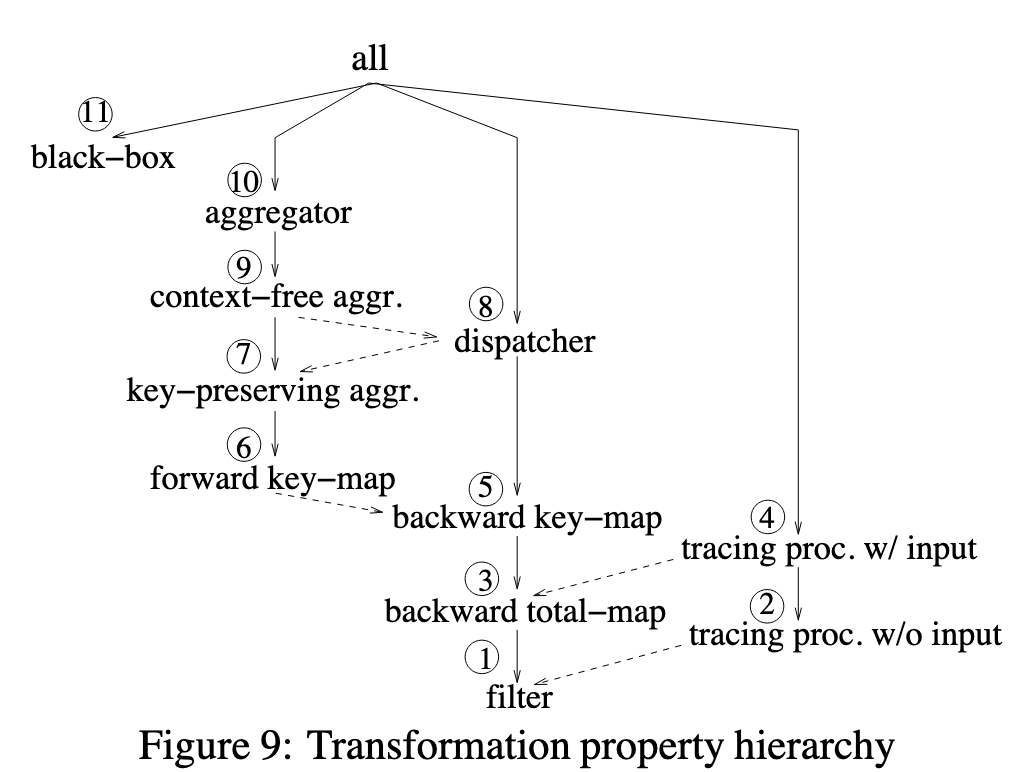
Authors consider three kinds of transformation properties, listed below. If a transformation exhibits multiple properties, then the best one is used for lineage tracing, based on a property hierachy.
- Each transformation is in a transformation class, based on how it maps input data items to output items.
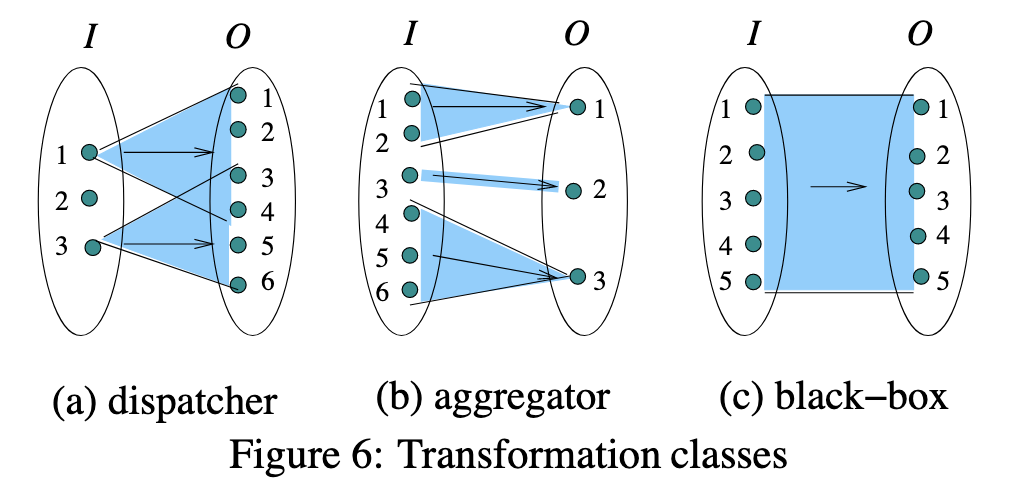
- dispatchers
- aggregators
- black-boxes
- Each transformation has one or more schema mappings, specifying how certain output attributes relate to input attributes.
- A transformation can have a tracing procedure or inverse transformation.
Transformation sequence
A transformation sequence is first normalized, by combining transformations when appropriate. When data is loaded through the transformation sequence, necessary results are saved. Then one can trace the lineage of any output data item through the normalized transformation sequence using iterative tracing procedure.